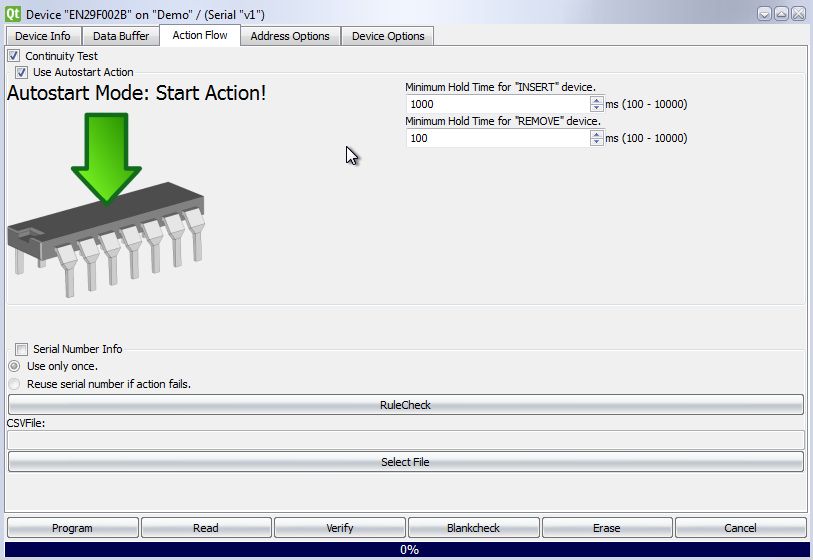
For some devices, special operations before or after a device action can be enabled or disabled under this tab.

When a device supports continuity test and insert/remove detection, the [Continuity Test] and [Autostart Action] check boxes are active.
[Continuity Test] checks if the device is correctly inserted and all socket pins are connected. Otherwise an error message will pop up at the beginning of a device action.
[Autostart Action] detects when a device is inserted, then starts the selected action automatically. This way a number of devices can be programmed without operating the GalepX user interface. In the [Minimum Hold Time] fields the detection time for inserting and removing devices can be given.
When [Serial Number] is activated, a serial number is programmed into the device memory at a specified address. The serial numbers must be stored in a simple text file, which can be specified under [Select File]. The [RuleCheck] button verifies that the file contains valid serial number format; its output appears in the Messages window.
The CSV (Comma Separated Values) serial numbers format is a semi-standard used by several industry programmers. It specifies serial numbers as well as text for labels to be printed on the device (GalepX does not print labels). Each line contains a record consisting of comma separated data in ASCII characters. The record defines a label or a serial number and its address in the device memory. Several lines can be combined for programming multiple serial numbers at different addresses.
A line in the CSV file looks like this:
Count (dec), SerialData (hex), SerialAddress (hex), DataLength (dec), RecordType [, Status]
Count is the number of the device. All records with the same number are programmed into the same device.
Status is the status information written by the GalepX software into the CSV file after programming the device. It consists of the characters p (pending), f (failed), u (used). F.i. pfpu means pending, failed, pending, used. If the status information is missing, the serial number record is unused.
RecordType is the way how the record is interpreted.
| R | Normal serial number data containing SerialData, SerialAddress and DataLength. |
| L | SerialData is used as label; SerialAddress and DataLength are ignored. |
| B | SerialData is used as label and serial number (together with SerialAddress und DataLength). |
2-byte hex numbers 0001 .. 0004 are written into address 07AA, labels "0001" .. "0003" are to be printed:
1, 0001, 7AA, 2, B 2, 0002, 7AA, 2, B 3, 0003, 7AA, 2, B 4, 0004, 7AA, 2, B
2-byte hex numbers 0001 .. 0004 are written into address 07AA, labels "1_7AA" ... "4_7AA" are to be printed:
1, 0001, 7AA, 2, R 1, 1_7AA, , , L 2, 0002, 7AA, 2, R 2, 2_7AA, , , L 3, 0003, 7AA, 2, R 3, 3_7AA, , , L 4, 0004, 7AA, 2, R 4, 4_7AA, , , L
2-byte hex numbers 0001 .. 0004 are written into address 07AA, 0011 .. 0044 are written into address 07BB, labels "1_7AA_7BB" ... "4_7AA_7BB" are to be printed:
1, 0001, 7AA, 2, R 1, 0011, 7BB, 2, R 1, 1_7AA_7BB, , , L 2, 0002, 7AA, 2, R 2, 0022, 7BB, 2, R 2, 2_7AA_7BB, , , L 3, 0003, 7AA, 2, R 3, 0033, 7BB, 2, R 3, 3_7AA_7BB, , , L 4, 0004, 7AA, 2, R 4, 0044, 7BB, 2, R 4, 4_7AA_7BB, , , L
► latest version online